V.35 Bus: This bus was discontinued, replaced by V.10/V.11 standard in 1989.
VAN: The Vehicle Area Network is an automotive bus developed by Peugeot and Renault. The VAN bus is a differential bus with Enhanced Manchester Data encoding having one or more Masters and some number of Slaves. The VAN Networking Topology may be either a BUS, Ring, Tree or Star style using broadcast or point-to-point communications. ISO standard 11519-3 [VAN Protocol]. Transmission speed 160kHz [estimate]. IC Interface MTC-30521, Alcatel. VAN Data Link Controller TSS461F, Atmel}
VAX Buses [Digital Equipment Corp.], are not currently listed on this site. VAX buses include DR11W, DRV11, Q-Bus, Unibus. VAX interfaces were superseded in the 1990's by the Alpha computer lines, and then discontinued in the early 2000's. VAX and MicroVax were never used as personal computers.
Velocity Interface Mezzanine {VIM} bus provides a dedicated data channel of up to 400 MB/sec to each of four processors on a quad processor 6U VMEbus board. Four 160-pin processor node connectors allow peripherals to deliver data directly to the private resources of each processor. Pentek developed this proprietary bus used on their cards.
VERSAbus: A backplane bus defined by Motorola Corporation in 1979 for its 68000 microprocessor.
VGA: Video Graphics Array is a superset of EGA, incorporating all EGA modes. Older displays sent digital signals to the monitor, while VGA (and later) send analog signals.
Video Buses {Video Buses; S-Video, Component/Composite Video, RS170, SCART, DVI}
VLB: The OBSOLETE VESA [Video Electronic Standards Association] Local bus [VLB or VL-Bus]: 33MHz @ 16/32 data bits, 30 address bits; PC Local Bus Expansion. Maximum of 3 devices on the bus. The VLB resides on a 16-bit ISA card with the VESA pins residing after the ISA pins, allowing an ISA card to use the same slot.
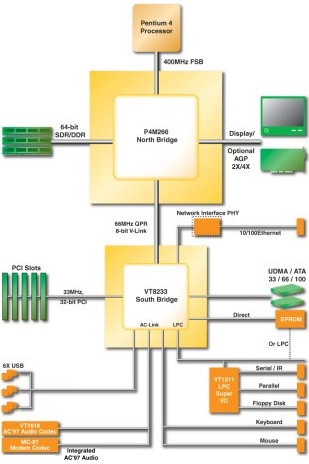
V-Link: VIA Technologies, Inc. uses V-Link as a narrow high-speed local interface between its north and south bridge chips that can sustain 266MB/s peak burst bandwidth.
VLYNQ : Texas Instruments uses the proprietary VLYNQ bus in it's broadband products, such as modems and wireless local area networks (WLANs); voice broadband processors, digital media processors, and OMAP media processor chips.
VMChannel: VESA Media Channel describes a hardware interface for desktop multimedia systems. VMChannel is a multiple master, multiple drop, clock synchronous interface designed for concurrent pixel data streams. VMChannel enables the real time flow of un-compressed multimedia pixels in a bidirectional fashion between multiple video adapters.
VME Bus: {VMEbus description}.
VME add-on Bus(s) {SkyChannel - RACEWay - Infiniband - P2CI - FPDP - Autobahn}
VPX {The new generation in VME Buses}
VXI Bus {VXIbus, VME for Instrumentation}
Next Bus Section Electronic Buses 'W'
An alphabetic listing of released interface buses. Primarily the links point to pages that describe the physical and electrical interfaces. Interface Bus protocols are not addressed.